The short answer to what is prosthodontics is that it's a specialized branch of dentistry recognized by the American Dental Association (ADA) that uses artificial devices to restore and replace missing or damaged teeth. Now let's dive into the long answer and really break down what is prosthodontics.
What is Prosthodontics, and What Do Prosthodontists Do?
Prosthodontists are experts in their field and have extensive training in various procedures aimed at preserving and enhancing the oral and maxillofacial tissues. This field seeks to improve dental function, health, appearance, and overall well-being for those with complex dental and facial matters.
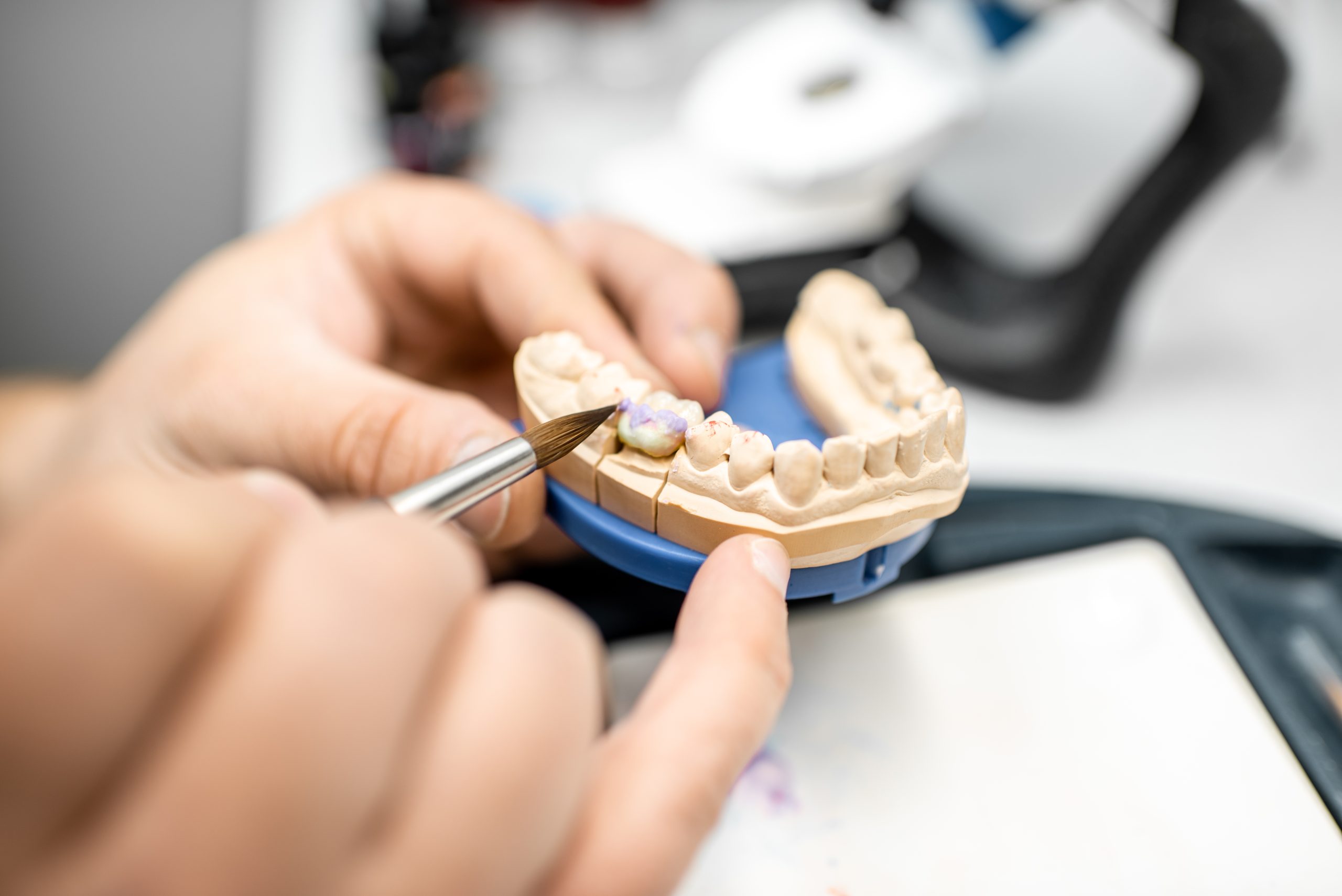
One of the essential services provided by prosthodontists is crafting and fitting dental prosthetics, such as crowns, bridges, and dentures. Crowns, also known as caps, are used to cover and strengthen damaged teeth, while bridges and dentures replace missing teeth and help maintain the functional aspects of the jaw. In some cases, prosthodontists also provide dental implants, a more permanent solution for tooth replacement.
Prosthodontics is the only dental specialty with a cosmetic and esthetic dentistry concentration. While general dentists may perform some simple cosmetic procedures, prosthodontists are more equipped to handle complex cases, such as smile makeovers and full-mouth reconstructions.
While not all prosthodontists specialize in orthodontics, some may provide braces or other orthodontic treatments. These interventions help correct alignment issues and improve oral health.
Education and Certification
Becoming a prosthodontist requires a commitment to extensive education, training and certification. This rigorous journey ensures that prosthodontists are adequately prepared to provide specialized dental care to their patients, restoring both function and aesthetics to their smiles.

Education and Training
In order to become a prosthodontist, individuals must complete several years of advanced education and training.
The first step in this educational journey typically involves obtaining a bachelor's degree with a concentration on science, such as biology, chemistry, and physics courses. These foundational subjects are critical for dental education as they provide a comprehensive understanding of the basic sciences and head and neck anatomy relevant to the field.
Aspiring prosthodontists must enroll in dental school after completing a bachelor's degree. Dental school is a four-year graduate program that provides theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience in dental surgery, as well as other dental specialties. Upon finishing dental school, students earn a Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) degree.
The next phase in training is a three-year prosthodontic graduate program, which focuses on advanced education in the field of prosthodontics. This program, often referred to as a residency, provides specialty training in various treatments such as dentures, dental implants, crowns, and bridges. It also includes advanced coursework in the basic sciences, head and neck anatomy, and dental surgery.
Throughout the advanced education program, prosthodontics residents work alongside experienced professionals, honing their skills and expanding their knowledge. They learn to assess, diagnose, and treat complex dental issues, ultimately becoming proficient in providing comprehensive, high-quality dental care.
Certification and Boards
Prosthodontics is identified by the American Dental Association (ADA) National Commission on Recognition of Dental Specialties and Certifying Boards. To become a certified prosthodontist, one must undergo specialized education and pass an examination process.
The American Board of Prosthodontics (ABP) is the leading authority responsible for board certification in prosthodontics. Becoming a Board Certified Prosthodontist involves completing dental school and an additional three or more years of prosthodontics residency. After the completion of their residency, candidates are required to pass a rigorous four-part examination conducted by the ABP.
In addition to the ABP, the American College of Prosthodontists (ACP) also plays a significant role in the field of prosthodontics. The ACP is an organization that supports the growth, development, and distribution of high-quality prosthodontic education. They collaborate closely with the ABP to maintain high education and certification standards for prosthodontists.
Board certification in prosthodontics not only demonstrates a specialist's expertise and commitment to their field but also ensures that they can provide the highest quality of care to their patients. By achieving board certification from organizations like the ABP and ACP, prosthodontists are recognized as specialists by the ADA and are more likely to stay updated with the latest advancements in prosthodontics.
Treatment Planning and Maintenance
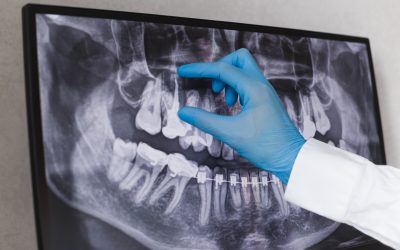
The first step in prosthodontic treatment is a thorough diagnosis. This involves thoroughly examining the patient's oral cavity, facial structures, and overall health. Through the use of dental imaging, such as X-rays and scans, the prosthodontist can assess the underlying bone structure and identify any potential issues that need to be addressed during treatment.
With a comprehensive understanding of the patient's specific needs and concerns, the prosthodontist then develops a dental treatment plan. This plan includes the selection of appropriate restorative treatments, depending on the patient's unique situation. The prosthodontist carefully considers various factors, including tooth and tissue conditions, esthetics, and functional needs, to ensure that optimal results are achieved.
Once the treatment plan is in place, the prosthodontist coordinates and oversees all patient care aspects. This may involve collaborating with other dental specialists, such as periodontists or oral surgeons, to address any additional concerns that may arise during the process. Close communication between all members of the dental team is essential to ensure that the patient's treatment plan is executed smoothly and effectively.
Maintenance plays a crucial role in supporting the success of restorative treatment and preserving the patient's oral health. Prosthodontists provide patients with the necessary knowledge and instructions for maintaining their dental work. This may include employing effective oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, and attending routine dental check-ups to monitor the health of the restored teeth and surrounding tissues.
Dental Restoration Types
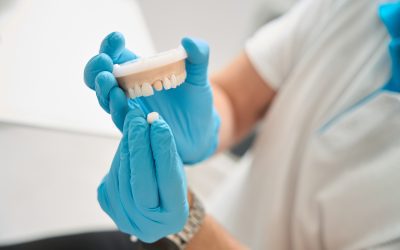
There are several types of dental restorations, which include crowns, bridges, implants, removable partial dentures, inlays, and more. This section aims to overview these types of dental restorations briefly.
Fixed prosthodontics involve dental restorations that are permanently attached to the teeth or gums. This category includes crowns and bridges, as well as other options like dental implants and veneers. These types of restorations provide a stable and natural-looking solution for patients who have lost one or more teeth.
Crowns are used to cover a damaged or weakened tooth, improving its strength, appearance, and functionality. They can be made from various materials, such as metal, porcelain, or both. Crowns are commonly used for teeth that are cracked, worn down, or vulnerable after a root canal treatment.
Bridges are dental prostheses used to replace one or more missing teeth. They are compromised of a series of connected crowns, where the outer crowns attach to the healthy teeth on either side of the gap, while the inner crowns fill the space left by the missing teeth. Bridges help restore chewing function and maintain the alignment of the remaining teeth.
Dental implants are positioned into the jawbone surgically and serve as an anchor for artificial teeth, such as crowns or bridges. They provide a secure and long-lasting foundation for the replacement tooth, ensuring optimal functionality and improved appearance.
Removable partial dentures are dental appliances designed to replace one or more missing teeth. These artificial teeth are connected to a base with matching gum coloring and held in position by metal clasps that fasten to the remaining natural teeth. Removable partial dentures are ideal for easier cleaning and maintenance purposes.
Inlays are a type of indirect dental restoration used to repair a tooth with mild to moderate decay or damage. They are custom-made to fit precisely into the prepared cavity and then cemented into place. Inlays are an alternative to traditional fillings, as they involve less removal of the tooth structure and can be made from more durable materials.
Each dental restoration type presents its own set of benefits and limitations. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a prosthodontist or dentist to determine the best option for your specific needs.
Complex Dental Cases
Prosthodontists are experts in handling complex dental cases, which often involve rehabilitation and full mouth reconstruction. Due to their extensive training, these specialists are well-equipped to treat a variety of issues.
One of the primary focuses of maxillofacial prosthodontists, a subset of prosthodontics, is the treatment of congenital disorders, which are conditions present at birth. These may include cleft palate, missing teeth, or irregular tooth and jaw development. Prosthodontists collaborate with other dental specialists to customize treatment plans addressing the unique needs of these patients.
Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) are another area in which prosthodontists specialize. TMD involves problems with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and surrounding muscles, causing pain in the jaw, face, and neck, as well as difficulty with jaw movements. Prosthodontists can offer oral splints and night guards. These devices are designed to alleviate discomfort, avoiding further damage to the teeth and jaw from conditions like bruxism (teeth grinding) or TMJ disorders.

Affordable Custom Nightguards
Oral cancer can be a life-altering diagnosis, often requiring extensive treatments and surgeries. Prosthodontists play a crucial role in the rehabilitation process after oral cancer treatment. They work closely with surgeons, oncologists, and other healthcare professionals to restore function and appearance to the mouth and jaw. This process may involve the use of dental implants, dentures, and other prosthetic devices. Additionally, prosthodontists assist with facial reconstruction resulting from trauma or injury, and they are trained in a variety of restorative procedures, such as bonding, bridges, and bone grafts.
In summary, prosthodontists have the skills and knowledge to address complex dental cases involving rehabilitation, full mouth reconstruction, congenital disorders, temporomandibular disorders, and oral cancer. Their expertise in the field allows them to provide compassionate, comprehensive care to patients with diverse needs, helping to restore function and appearance and improve their quality of life.
Cosmetics and Appearance
Prosthodontics plays a significant role in enhancing the aesthetics of a person's smile by addressing damaged or missing teeth. Cosmetic dentistry often overlaps with prosthodontics in terms of the treatments offered to improve a patient's appearance.
One of the widely recognized procedures in cosmetic dentistry is the application of dental veneers. Dental veneers are thin, customized shells made from porcelain or composite materials designed to cover the front surface of the teeth. These veneers help improve the appearance of discolored, chipped, or misaligned teeth by providing a natural, healthy-looking smile.
Prosthodontists have the expertise to create state-of-the-art dental veneers to give patients the desired cosmetic results. Using advanced technology, they can replicate the natural appearance of the tooth enamel while ensuring the veneers fit seamlessly over the existing teeth.
In addition to veneers, prosthodontists handle other dental procedures aimed at improving cosmetics and appearance. These procedures include dental implants, crowns, bridges, and oral splints, all of which serve to replace or restore damaged or missing teeth, enhancing the smile's overall appearance. Prosthodontists also fit and place dental implants, offering patients a long-lasting and secure solution to tooth loss.
While not all prosthodontists specialize in orthodontics, some may provide braces or other orthodontic treatments. These interventions help correct alignment issues and improve oral health.
Achieving aesthetically pleasing results for patients is a top priority for prosthodontists. With their extensive training and knowledge in the field, they are equipped to offer dental treatments that not only restore function but also create beautiful and natural-looking smiles.
Prosthodontics Technology and Procedures
Prosthodontists are trained to utilize state-of-the-art techniques and advanced technology to address complex dental needs and enhance their patients' oral health and appearance.
One of the key areas in prosthodontics is implantology, which involves the placement of dental implants to replace missing teeth. Dental implants are artificial titanium tooth roots which are surgically inserted into the jawbone. They provide a strong foundation for fixed or removable replacement teeth, offering a more stable and durable solution compared to traditional dentures or bridges.
Prosthodontists also employ various advanced procedures to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their treatments. For instance, they may use computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology to produce precise and customized dental restorations like crowns, bridges, and veneers. This technology enables the prosthodontist to develop highly accurate restorations, significantly reducing the time and number of visits required by the patient.
In recent years, digital dentistry has become an integral part of prosthodontics. Prosthodontists can use innovations like intraoral scanners, digital impressions, and 3D printing to create more accurate models of their patients' mouths. This enables better treatment planning and execution, resulting in improved patient outcomes and shorter treatment periods.
Another vital aspect of prosthodontic technology is the use of dental materials specifically designed to meet the various needs and desires of the patients. With a comprehensive understanding of these materials, prosthodontists can select the most suitable options for each case, ensuring a comfortable fit, enhanced durability, and optimal aesthetics.
Overall, prosthodontic technology and procedures constantly evolve to provide more comprehensive and efficient treatment solutions for patients with complex dental needs. Through the use of cutting-edge techniques and materials, prosthodontists can restore not only the function but also the appearance of their patient's smiles, significantly improving their overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a prosthodontist do?
A prosthodontist is a dentist who provides specialized solutions using artificial devices to replace damaged or missing teeth, thus alleviating pain and improving the patient's overall well-being. They are experts in creating dental prostheses, ranging from simple crowns to full-mouth rehabilitation using dental implants.
Prosthodontist vs orthodontist
While both prosthodontists and orthodontists are dental specialists, they focus on different aspects of dental care. An orthodontist primarily deals with dental and facial irregularities diagnosis, prevention, and treatments, such as crooked teeth, misaligned bites, and jaw-related issues. On the other hand, a prosthodontist addresses complex dental restoration challenges, such as replacing missing teeth, improving the aesthetics of the smile, and reconstructing damaged oral structures.
Prosthodontist vs periodontist
Again, both prosthodontists and periodontists are dental specialists, but they focus on different areas. A periodontist is primarily concerned with the health of the supporting structures surrounding the teeth, including gums. In contrast, a prosthodontist uses artificial devices to restore and replace damaged or missing teeth.
How to become a prosthodontist
To become a prosthodontist, a dentist must first complete a dental degree and obtain a valid dental license. Afterward, they must pursue at least 34 months of additional, full-time clinical training in prosthodontics, which is typically carried out in a school or hospital setting.
Is prosthodontics related to dental implants?
Yes, prosthodontics is closely related to dental implants. Prosthodontists specialize in the design, placement, and maintenance of implants and other dental prostheses. They play a critical role in creating an aesthetically pleasing and functional dental implant solution for patients who have lost one or more teeth.
Cost of prosthodontist services
The cost of prosthodontist services can vary depending on the treatment's complexity and the patient's specific needs. Generally, prosthodontic procedures can be more expensive than general dentistry due to the specialized training and expertise required for these complex treatments. It is important to consult with a prosthodontist to discuss treatment options and associated costs.